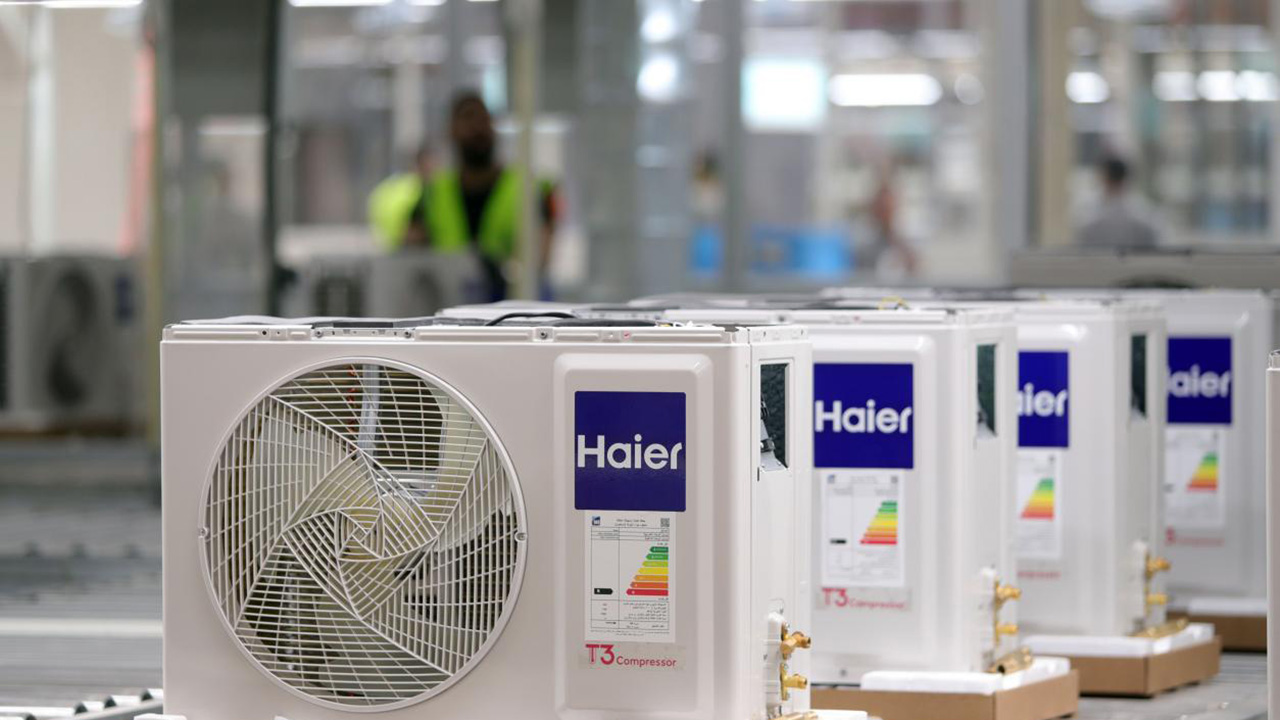
Household Air-Conditioner Outdoor-Unit Assembly Line—Smart Air-Conditioner Assembly Line
Description
We specialize in providing comprehensive solutions for Air Conditioners Assembly Lines/Production Lines.
Air Conditioner Assembly Lines/Production Lines are Suitable to Assemble/Produce Air Conditioners.(Welcome to contact us, we will suggest and design the suitable Assembly Lines/Production Lines for your Air conditioners.)

Household Air-Conditioner Outdoor-Unit Assembly Line introduction
1. Basic Definition
A residential air-conditioner outdoor-unit assembly line is a continuous conveyor system that automatically or semi-automatically builds complete outdoor units from components such as compressors, condensers, fan assemblies, valve sets, and sheet-metal housings. It is designed for high tact time, high quality, and mixed-model production.
2. Line Configuration & Key Technologies
– **Conveying Media**
Slat-chain conveyor (carrying 20–30 kg bare chassis), roller transfer sections, and non-powered return pallet loop; premium lines use “pallet + lift-and-transfer” zero-back-pressure accumulation and support pallet-free chassis flow.
– **Automatic Feeding**
AGVs or lifters deliver compressors and fin-and-tube condensers to the stations; a 6-axis robot with 3-D vision picks up a 20 kg compressor and completes code-scanning, positioning, and seating within 12 s.
– **Critical Assembly Stations**
1. Chassis pre-assembly: rivet feet, stick damping pads.
2. Compressor mounting: robot tightens four high-strength bolts to 45 N·m ± 1 N·m.
3. Condenser tube insertion: servo slide pushes U-tubes in, followed by flaring and on-line eddy-current flaw detection.
4. Automatic brazing: nitrogen-protected, three-position rotary table using flame or high-frequency brazing; vision checks weld fillet after brazing.
5. Helium leak test: vacuum chamber + sniffer mode; leak rate ≤ 1 g/y for automatic pass.
6. Vacuum & refrigerant charge: dual-stage pump down to 30 Pa background, R32/R410A mass-flow charging with ± 1 g accuracy.
7. Electrical & 4-way valve wiring: collaborative robot inserts terminals with force feedback to prevent half-mating.
8. Fan set-up: automatic blade pressing; height detection and initial dynamic balance screening.
9. Housing closure: right panel, valve plate, and top cover are screwed in sequence; smart driver stores torque curve.
10. Running test: 85 % rated voltage low-voltage start, cooling & heating modes; test data closed-loop uploaded to KB line computer.
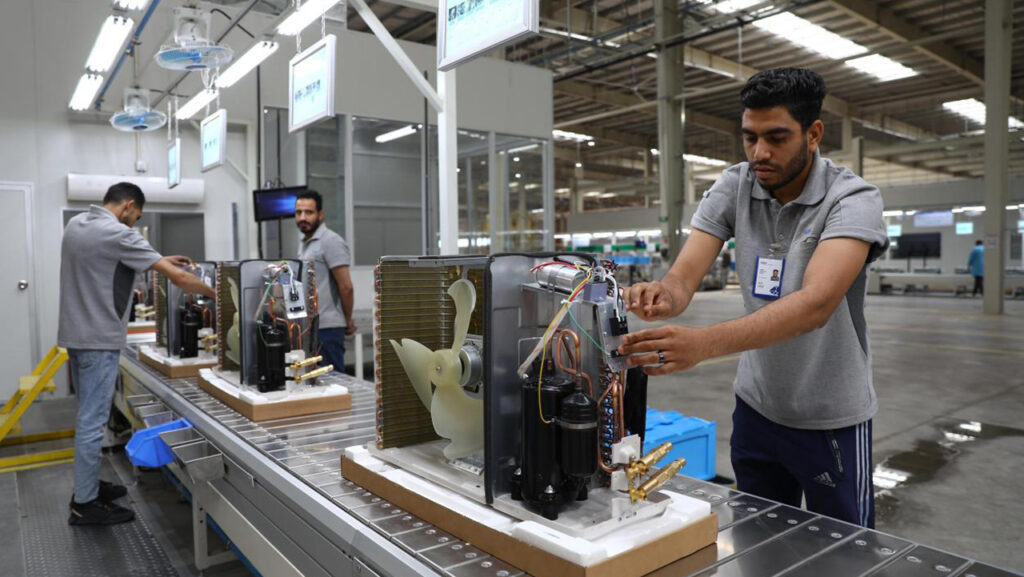

– **Traceability**
Full-line barcode scanning; critical torque, pressure, vacuum, refrigerant weight, and test data are written to MES in real time, enabling unit-level traceability.
3. Typical End-to-End Flow
Chassis loading → rivet feet → robot compressor mount → condenser tube insert → auto-braze → helium leak test → vacuum → refrigerant charge → fan assembly → electrical wiring → housing close → running check → nameplate → auto-bagging → robot palletizing → automated warehouse.
4. Development Trends
– **AI vision QC**: real-time judgement of weld, missing screw, or casing scratch; false reject reduced by another 50 %.
– **Digital twin**: whole-line simulation synchronized with physical status; predictive maintenance cuts downtime by 15–20 %.
– **Green-refrigerant adaptation**: R290 explosion-proof environment; AGVs, robots, and sensors carry full Ex certification.
– **Flexible island mode**: assembly–test–pack split into movable islands, allowing capacity to be ramped up or down rapidly according to order volume.